Fine Tuning
A fine tuning project for smart forms
Project Overview
Form filling is a common task that can be automated using Large Language Models (LLMs). This project focuses on developing a system that can automatically extract relevant information from unstructured text and populate HTML form fields intelligently.
The system may works in two ways:
Text Copy-Paste: Users can copy text from any source (emails, documents, etc.) and paste it into the form.
Speech-to-Text: Users can speak the information, which gets converted to text and then pasted into the form.
How It Works
Input Processing: Copied text directly or convert speech to text using Speech Recognition.
LLM Processing: The text is sent to an LLM which identifies and extracts relevant information like names, dates, addresses, and other structured data.
Form Population: The extracted information is mapped to corresponding form fields, automatically filling the form. Users can review and edit the results.
Demo Application
I have created a demo Angular application to test the copy-paste functionality sending the text to an LLM.
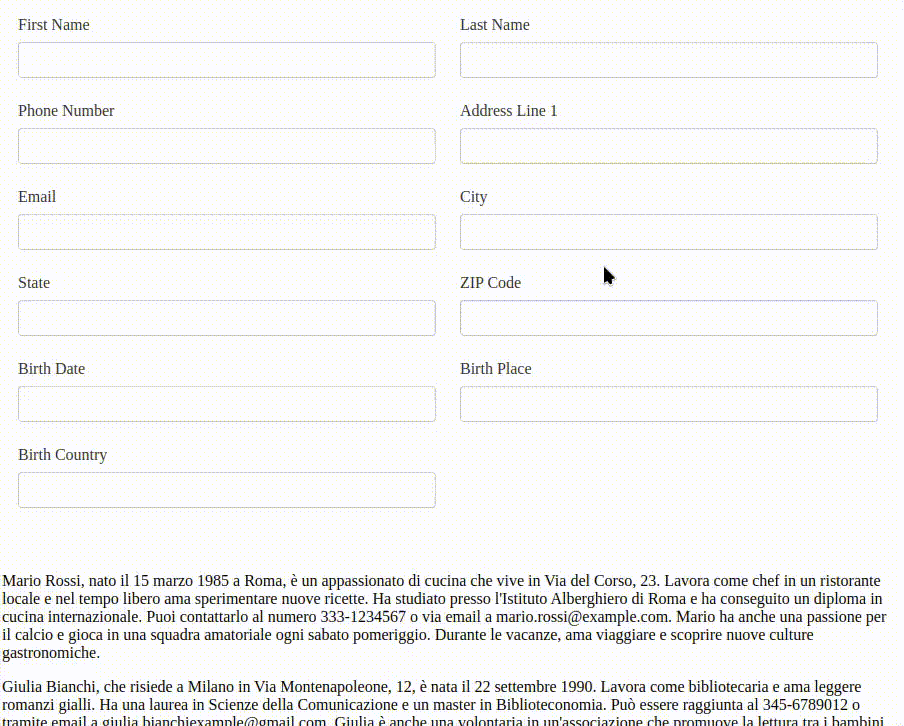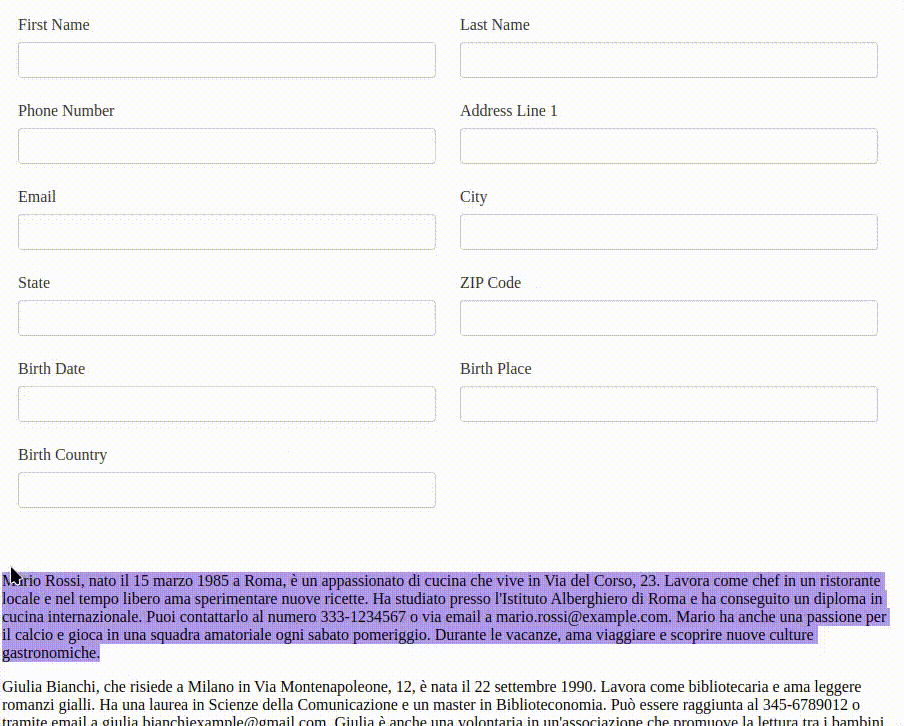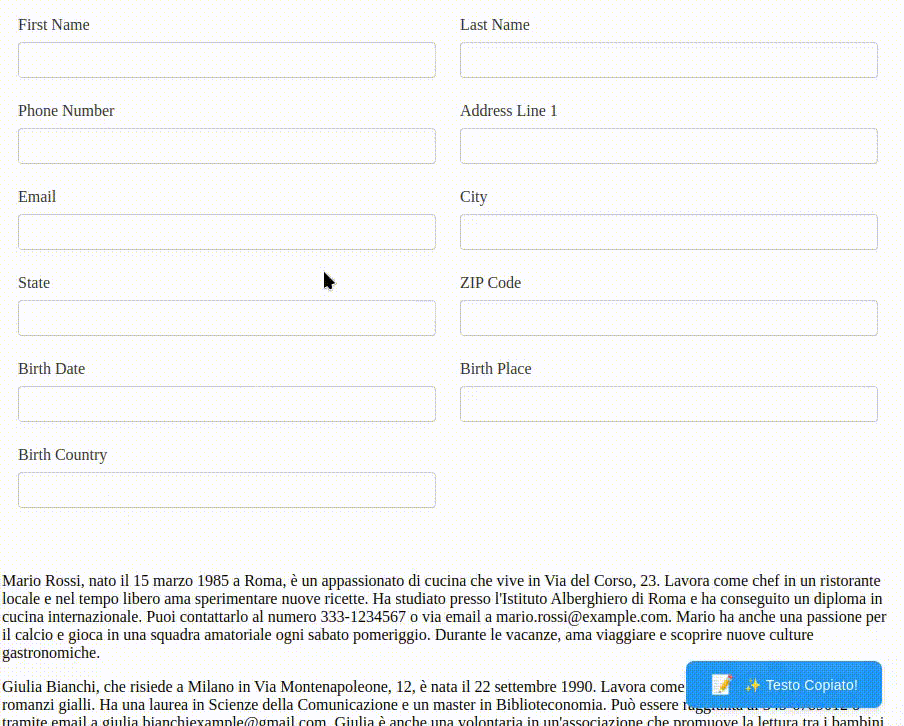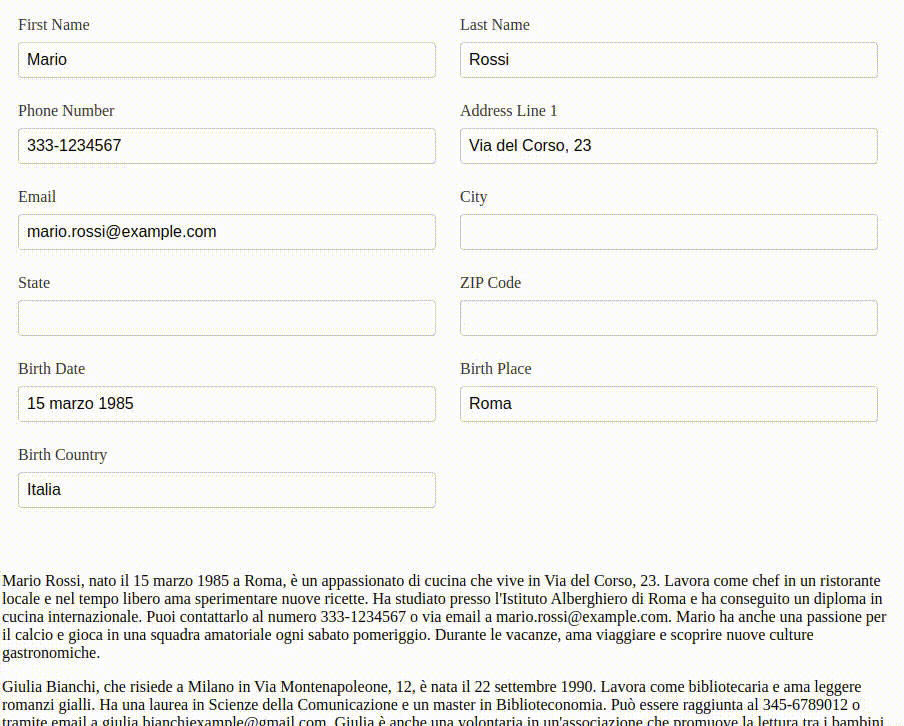 A demonstration of the text copy-paste functionality
A demonstration of the text copy-paste functionality
The demo application can use any LLM model to extract the information by the text, because have created backends for OpenAI, Mistral and LLaMA APIs in the Angular form-filler backends library, inspired by the smart-form-filler project.
Testing with canonical LLM models has shown very good results. I have tested with gpt-3.5-turbo llama3.1-8b and mistral-large-latest. While all models perform well, gpt-3.5-turbo tends to provide slightly more accurate field extraction compared to llama3.1-8b and mistral-large-latest, though both produce satisfactory results for form-filling purposes. So one can experiment with different models to find the best suitable model for the task.
You can find the demo application in GitHub project smart form.
System prompt
For testing purposes, I used the same system prompt across all LLM backends (OpenAI, Mistral, and LLaMA) to ensure a fair comparison of their capabilities. This standardized approach helps maintain consistency in how each model processes and extracts information from the input text.
the prompt is the same generic prompt from the smart-form-filler project.
system prompt pseudocode:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
"role": "system",
"content": """Each response line matches the following format:FIELD identifier^^^value
Give a response with the following lines only, with values inferred from USER_DATA:
FIELD firstName^^^The firstName of type string
FIELD lastName^^^The lastName of type string
FIELD phoneNumber^^^The phoneNumber of type string
FIELD addressLine1^^^The addressLine1 of type string
FIELD addressLine2^^^The addressLine2 of type string
FIELD email^^^The email of type string
FIELD city^^^The city of type string
FIELD state^^^The state of type string
FIELD zip^^^The zip of type string
FIELD country^^^The country of type string
FIELD birthDate^^^The birthDate of type string
FIELD birthPlace^^^The birthPlace of type string
FIELD birthCountry^^^The birthCountry of type string
END_RESPONSE
Do not explain how the values were determined. # to not diverge by the task
Trying to deduce state where do he lives. # this is a hint for the LLM to deduce the living state
Trying to deduce birth country also. # this is a hint for the LLM to deduce the birth country
For fields without any corresponding information in USER_DATA, use value NO_DATA.
The fields list can be build dynamically reading the form fields, so can be adapted to any form type.
User prompt
the user prompt is the text copied by the user or the speech converted to text, and can be formatted in this simple way:
1
2
3
"role": "user",
"content": """USER_DATA: <text>""" # Sono Mario Rossi e vivo a Milano da tre anni...
LLM response
After sending the prompts to the LLM, via API, the response will be in the following format:
1
2
3
4
"role": "assistant",
"content": """FIELD firstName^^^Mario
FIELD lastName^^^Rossi
FIELD addressLine1^^^....
So it’s straightforward to parse the response and populate the form fields!
Using private/local LLM models
The system can be extended to use private/local LLM models by adding a new backend for the local model and a new form-filler backend.
Why use private/local LLM models?
- For privacy reasons, because user data is not sent to the cloud, so it’s private and secure.
- For cost reasons, we can use a small local model, specialized in this task, so it can be cheaper.
I have tested two small models:
Llama-3.2 in 1B and 3B versions, downloaded from Hugging Face.
I have choosen 1B and 3B versions because I’m curious about the small model’s performances, and want to use locally on economic PCs.
I used instruct versions because they are already trained on chat templates, and can be more suitable for specific task-oriented applications.
the Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct performs poorly, having a lot of NO_DATA in the responses:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
FIELD address^^^Via Roma, 12
FIELD property_type^^^Monolocale
FIELD size^^^40
FIELD kitchen^^^NO_DATA
FIELD bathroom_window^^^NO_DATA
FIELD floor^^^2
FIELD elevator^^^NO_DATA
Sometimes the model repeats the fields in the response:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Nominativo^^^Maria
Residenza^^^Toscana
Descrizione_casa^^^Una casa rustica
Passatempo_preferito^^^Leggere
END_RESPONSE
Nominativo^^^Maria
Residenza^^^Toscana
Descrizione_casa^^^Una casa rustica
Passatempo_preferito^^^Leggere
END_RESPONSE
Nominativo^^^Maria
Residenza^^^Toscana
Descrizione_casa^^^Una casa rustica
Passatempo_preferito^^^Leggere
END_RESPONSE
With the 3B model the performance is much better, reduced the NO_DATA and the responses formats are substantially correct.
We want to fine-tune the models to see if we can improve the model performances.
Fine-tuning
The idea is to fine-tune the models using a synthetic dataset created by a larger LLM (gpt-3.5-turbo)
We use axolotl to fine-tune the models on a dual GPU NVIDIA RTX 3090 (24GB VRAM on each card) PC using a synthetic dataset created by the large gpt-3.5-turbo model.
Synthetic dataset creation
We need a dataset containing generic texts that can be used across various HTML forms. We consider, ideally: user data forms, clinical cases, gym card plans, hotel bookings, taxes forms, etc.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
system_prompt = """
You are an AI assistant that extracts structured data from text.
So you must individuate relevant data from the text that must be used to fill various form fields.
You need to nominate the fields that you are extracting.
You must generate json objects that can be used to test an AI assistant that extracts structured data from text.
The json object must be in the following format:
{ text: "text", form_fields: [{"name": "field_name", "type": "field_type", "value": "field_value"}, ...] }
field names must be in english, do not contain spaces or special characters.
You prefer name, surname instead of fullname for fields that are related to a person.
The text can be a description of a person, a clinical case, a gym card plan, an hotel booking, a taxes form, etc.
Don't use description of persons only!
The text must be in Italian.
The text must be at most 300 words.
Variate the text to test the AI assistant in different ways.
generate 3 different texts, separate them with a pipe | symbol
"""
As you can see, to variate texts, we generate 3 different texts, separated by the pipe symbol.
Another approach to variate generated texts is to define different scenarios, features, users and generate texts for each combination of them.
for further info see the excellent articles by Hamel Husain: A framework for generating realistic test data
So we execute the following command n times (10000 times, or more) to create the dataset:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
response = client.chat.completions.create(
#model="gpt-4o",
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
# {"role": "user", "content": prompt}
],
max_tokens=3000,
n=1,
response_format={ "type": "text" },
stop=None,
temperature=1.0
)
content = response.choices[0].message.content
Choose temperature=1.0 to maximize the creativity of LLM.
Theorically if execute the command 10k times, we will have a dataset of 30k texts, but in practice will have a minor number of texts, because sometimes the LLM will generate texts that are not valid, during the iterations. (in my case it was capable of about 26k valid texts)
With some postprocessing we can transform the dataset to have only valid texts in openai valid format:
example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
{"messages":
[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "\nEach response line matches the following format:\nFIELD identifier^^^value\n\nGive a response with the following lines only, with values inferred from USER_DATA:\n\nFIELD name^^^The name of type text\nFIELD age^^^The age of type number\nFIELD height^^^The height of type number\nFIELD weight^^^The weight of type number\nFIELD symptoms^^^The symptoms of type text\nFIELD medical_condition^^^The medical_condition of type text\nEND_RESPONSE\n\nDo not explain how the values were determined.\nFor fields without any corresponding information in USER_DATA, use value NO_DATA.\n"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "\nUSER_DATA:Il paziente Marco ha 35 anni, è alto 180 cm e pesa 75 kg. Si è recato in ospedale per dolore al petto e affaticamento. Durante l'esame è emerso che ha la pressione alta e l'elettrocardiogramma ha mostrato anomalie. Sarà sottoposto a ulteriori controlli per valutare la sua condizione cardiaca.\n"
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "FIELD name^^^Marco\n\nFIELD age^^^35\n\nFIELD height^^^180\n\nFIELD weight^^^75\n\nFIELD symptoms^^^dolore al petto e affaticamento\n\nFIELD medical_condition^^^pressione alta, anomalie all'elettrocardiogramma\n"
}
]
}
now we can try to fine-tune the models, with 26k texts dataset in openai format.
Fine-tuning process with LoRA (low-rank adaptation)
Axolotl simplifies the process and provides simple commands to fine-tune the models, the settings file is config.yaml.
The dataset is in openai format and we explicitly mapped to the message_property_mappings and roles properties. We have choosen to split the dataset in 95% for training and 5% for validation (val_set_size).
We use LoRA fine tuning mode, with a rank of 32, alpha 16 and a random dropout of 5%. The tuned model will be saved in the ./outputs/lora-out folder.
To save memory usage we use 8bit quantization and a gradient accumulation steps of 4.
To speed up the process and use dual GPUs we use deepspeed with the zero1.json configuration and run axolotl via accelerate. Can link a wandb project wandb-project-name to the fine tuning process to monitor the process and the results.
To successfully run the fine tuning process on my machine I had to reduce the mini batch to 1.
In this example we perform training for 10 epochs and use a learning rate of 0.0002. However, the learning rate it’s not a fixed value, because the model is trained with adamw_bnb_8bit optimizer that uses a cosine learning rate scheduler. In substance the learning rate variates like cosine function.
in this example settings are for the Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct model, taken dataset from /path-to/dataset.jsonl file.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
base_model: meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct
model_type: LlamaForCausalLM
tokenizer_type: AutoTokenizer
load_in_8bit: true
load_in_4bit: false
strict: false
datasets:
- path: /path-to/dataset.jsonl
type: chat_template
field_messages: messages
message_property_mappings:
role: role
content: content
roles:
system:
- system
user:
- user
assistant:
- assistant
dataset_prepared_path:
val_set_size: 0.05
output_dir: ./outputs/lora-out
sequence_len: 4096
sample_packing: true
eval_sample_packing: false
pad_to_sequence_len: true
adapter: lora
lora_model_dir:
lora_r: 32
lora_alpha: 16
lora_dropout: 0.05
lora_target_linear: true
lora_fan_in_fan_out:
lora_modules_to_save:
- embed_tokens
- lm_head
wandb_project: wandb-project-name
wandb_entity:
wandb_watch:
wandb_name:
wandb_log_model:
gradient_accumulation_steps: 4
micro_batch_size: 1
num_epochs: 10
optimizer: adamw_bnb_8bit
lr_scheduler: cosine
learning_rate: 0.0002
train_on_inputs: false
group_by_length: false
bf16: auto
fp16:
tf32: false
gradient_checkpointing: true
early_stopping_patience:
resume_from_checkpoint:
local_rank:
logging_steps: 1
xformers_attention:
flash_attention: true
s2_attention:
warmup_steps: 10
evals_per_epoch: 4
eval_table_size:
eval_max_new_tokens: 128
saves_per_epoch: 1
debug:
deepspeed: /path-to/axolotl/deepspeed_configs/zero1.json
weight_decay: 0.0
fsdp:
fsdp_config:
special_tokens:
pad_token: <|end_of_text|>
to run the fine tuning process we use the following command:
1
2
(env) [user@pc]$ export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2
(env) [user@pc]$ accelerate launch -m axolotl.cli.train config.yml
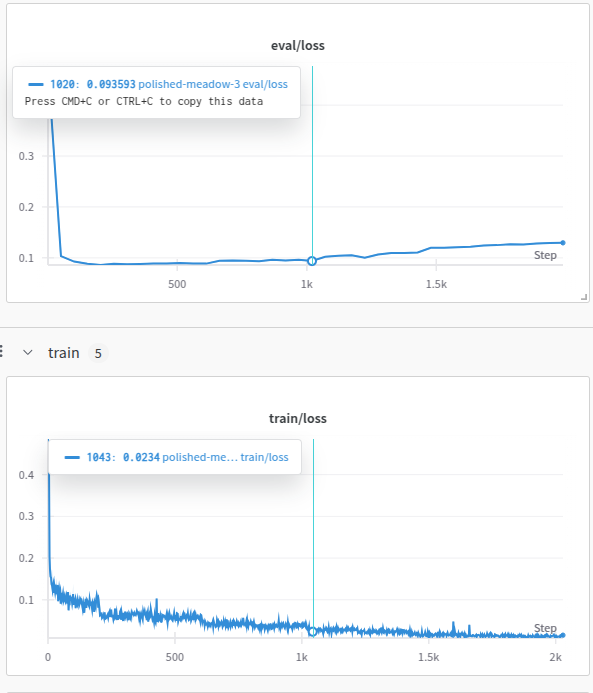
At the end of the fine tuning process have obtained these results:
The training loss on training set continues to decrease throughout the training cycle, but after 5 epochs the decrease is not significant. The evaluation loss on validation set is higher than the training loss, as usual, and after circa 5 epochs becomes to increase, so we could stop the training process after 5 epochs.
..to be continued